What’s Mass
Spectrometry?
Mass spectrometry is one of the most powerful techniques in chemical analysis. Mass spectrometers enable to detect and characterize substances based on the mass-to-charge ratio of their molecules. To do so, MS comprise two basic components: an ionization source and a mass analyzer.
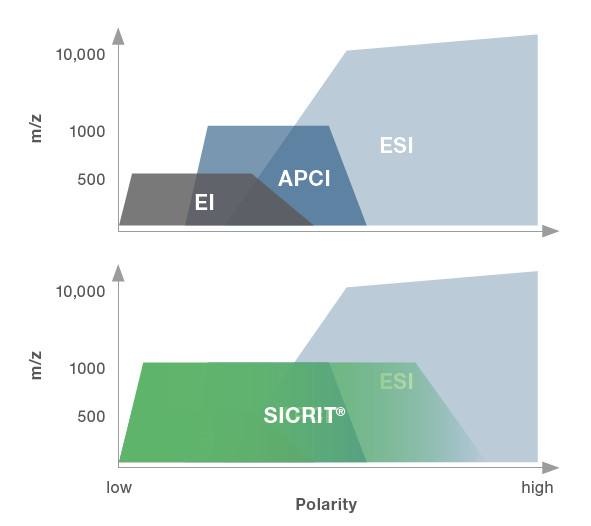
The SICRIT® Ion Source Technology is an ambient flow-through ionization technique (Soft Ionization by Chemical Reaction In Transfer) for mass spectrometers with atmospheric pressure inlet (LC-MS).
Ion Source
Technology
Head to Head Comparison
Conventional ionization
It is fundamentally different to conventional ionization methods:
In almost all conventional ionization methods like ESI, DART, DESI or APCI, the analyte gets ionized before being introduced into the MS.
SICRIT® ionization
The patented SICRIT® Ion Source Technology extends the inlet of the MS and ionizes all molecules that are drawn into the system due to the prevailing vacuum by means of a specially shaped cold plasma.
Ion Source
Advantages
Increased sensitivity
The ionization within a closed chamber in extension of the inlet prevents columbic repulsion before the inlet and enables higher sensitivities.
Enhanced range of analytes
Three simultaneous ionization mechanisms expand the range of detectable analytes, covering polar and non-polar components.
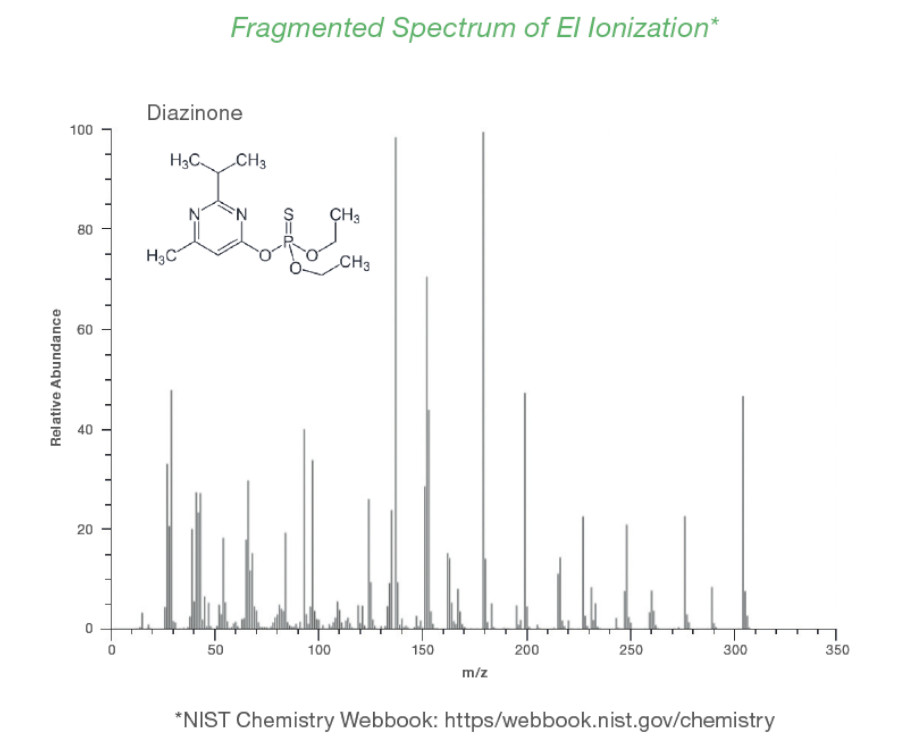
No fragmentation
The unique shape of the cold plasma enables a soft ionization of analytes and avoids fragmentation.
One for all
The SICRIT® source is available for all current LC-MS systems of all vendors.
No sample preparation
The ambient character of the ionization source allows to analyze solid, liquid, or gaseous samples in room air without sample preparation (direct screening).
Flexible coupling
SICRIT® ion source technology is the only technique that provides a seamless coupling with all chromatography methods like GC, LC and SFC.
Low operation costs
SICRIT® does not require Helium or other noble gases for operation, it runs with ambient air and electrical power.
Easy installation & operation
Plug & play ion source that does neither require calibration nor adaptions on hardware, software, or workflow.